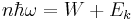Above threshold ionization
Within Atomic, molecular, and optical physics Above Threshold Ionization (ATI), which was first discovered in 1979[1], is a multi-photon effect where an atom is ionized with more than the required number of photons. ATI. In the case of ATI, the generalized Einstein formula applies
where  represents the number of photons absorbed,
represents the number of photons absorbed, 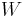 is the ionization energy (work function) and
is the ionization energy (work function) and 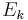 is the electron kinetic energy. This phenomenon is measurable only if the electromagnetic field is comparable with the field which keeps the electrons in the atom. Very strong laser sources, such as those used in ultrashort pulses, can create ATI features. With this method one can generate, for example, beta radiation. The photoelectron spectrum of electron energies is continuous since actual light sources contain a spread of energies. It typically has a very strong maxima for the minimum number of photons to ionize the system with successive peaks (known as ATI peaks) occurring at energies corresponding to higher numbers of photons being absorbed; every peak is then separated by the photon energy
is the electron kinetic energy. This phenomenon is measurable only if the electromagnetic field is comparable with the field which keeps the electrons in the atom. Very strong laser sources, such as those used in ultrashort pulses, can create ATI features. With this method one can generate, for example, beta radiation. The photoelectron spectrum of electron energies is continuous since actual light sources contain a spread of energies. It typically has a very strong maxima for the minimum number of photons to ionize the system with successive peaks (known as ATI peaks) occurring at energies corresponding to higher numbers of photons being absorbed; every peak is then separated by the photon energy 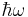 .[2]
.[2]
References
- ^ Bashkansky, M.; Bucksbaum, P., Schumacher, D. (13 June 1988). "Asymmetries in Above-Threshold Ionization". Physical Review Letters 60 (24): 2458–2461. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.60.2458.
- Agostini, P.; Fabre, F., Mainfray, G., Petite, G., Rahman, N. (23 April 1979). "Free-Free Transitions Following Six-Photon Ionization of Xenon Atoms". Physical Review Letters 42 (17): 1127–1130. doi:doi/10.1103/PhysRevLett.42.1127. The original paper on the discovery
- ^ Cormier, E; Lambropoulos, P (14 May 1996). "Optimal gauge and gauge invariance in non-perturbative time-dependent calculation of above-threshold ionization". Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics 29 (9): 1667–1680. doi:10.1088/0953-4075/29/9/013.
Links
Multiphoton ionization of the calcium atom by linearly and circularly polarized laser fields